|
|
ACL Rupture
The cruciate ligaments are formed in-utero before the joint surfaces and are pivotal for normal knee function - excuse the pun!
|
|
Football is the commonest cause, but any injury with full weight over a twisted knee can cause an ACL rupture.
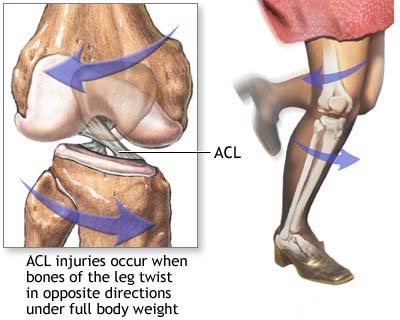
Diagnosis
Hx |
|
LOOK |
|
FEEL |
|
MOVE |
(There may be no detectable opening in a Grade 1 injury)
Exclude combined ACL+ Meniscal Detachment
Exclude combined ACL + MCL
Exclude combined ACL + PCL
Exclude combined ACL + PLC
|
XRAYS |
AP and Lateral views
Exclude combination injuries
|
MRI |
|
Emergency Room Treatment
Few of these patients will have multiligament injuries and will need an emergency orthopaedic referral. Please use the guidance on the referral form :-
© Mr Gavin Holt :: CotswoldClinics.com :: Print this frame