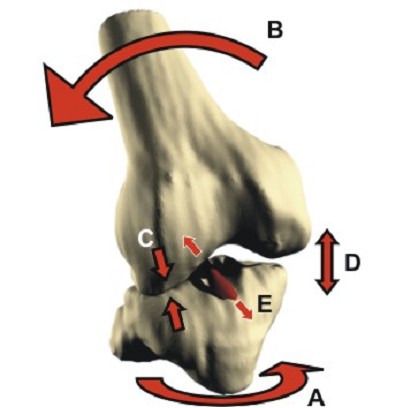
Meniscal Detachment
This term can be used to describe a high energy injury to the meniscus, usually in young patients. During the act of ligament rupture there is very rapid dissipation of energy with instantaneous displacement of the femur on the tibia "snap":-


This can cause severe damage to the meniscii either wrenching them from their attachment ("peripheral detachment") or by splitting off a large "bucket handle" segment. This is different to the common degenerative tear where a meniscus has gradually become weaker and weaker to finally fail following a trivial injury ("the straw that broke the Camel's back").
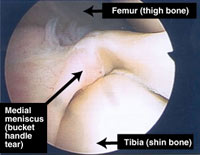
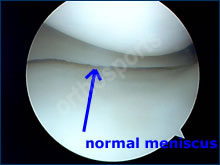
Bucket Handle Tear Normal
In young patients these injuries can be repaired reducing the risk of early osteoarthritis. It is important that they are recognised early to increase the success rate for repair. Meniscal detachment can accompany any pattern of ligament rupture :-
Ligament Injury |
Rate of Meniscal detachment |
MCL |
?? |
ACL |
|
PCL |
?? |
PLC |
?? |
Multiligament injury |
|
Diagnosis
Hx |
|
LOOK |
|
FEEL |
|
MOVE |
Exclude combined MCL + Meniscus
Exclude combined ACL + Meniscus
|
XRAYS |
AP and Lateral views
Exclude combination injuries
|
MRI |
This is the principle reason for MRI scans in ACL rupture - not to confirm the ACL rupture which is usually clinically obvious |
Emergency Room treatment
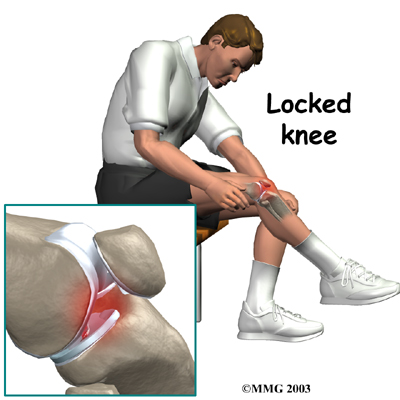
Treatment is usually dictated by the ligamentous injury. For an isolated "bucket handle tear" with a true locked knee:-
Specialist treatment
Meniscal detachments are amendable to repair with sutures if seen early. Once the femur has rolled over the meniscal fragment for a week or two it is too distorted to fix back in position. Additionally the longer this injury is left the poorer the healing capacity when the two parts are reunited.
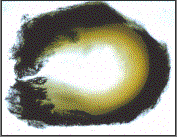
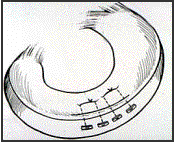
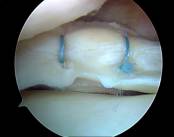
The blood supply to the meniscus is normally poor (hence degeneration with age) and failure of meniscal healing leads to failure of meniscal suturing in 10-30 percent of cases. Even with this relatively high rate of failure repair is recommended because the long term benefit for the successful cases is high, and the morbidity from a second arthroscopy and resection of the failed meniscal repairs is low.
Rehabilitation
As an isolated treatment meniscal repair should be protected from shear forces for 8 weeks. This means avoiding flexion beyond 100 degrees and excessive load bearing under flexion. Braces can be used for patients who find it difficult to comply.
When repaired as part of a ligament reconstruction the meniscus can usually be ignored as patients tend to protect the knee for the first 6-8 weeks and the risk of disrupting the meniscal repair is low.
© Mr Gavin Holt :: CotswoldClinics.com :: Print this frame